How are Smart Cities using technology to ‘Go Green’?
Green technologies are transforming urban life by providing intelligent and eco-friendly IT solutions that create harmony between city residents and the environment
What is a Smart City?
Cities around the globe are becoming smarter by using the latest technological innovations – mainly Big Data and ubiquitous internet connectivity – in order to improve their citizens’ lives.
Digital technologies can assist urban planners with making better and faster decisions related to energy efficiency, waste and water management, public transport, and sanitation.
With climate scientists increasingly stressing the importance of curbing greenhouse emissions and managing waste, a smart city is essentially an environmentally-conscious, ‘green city’.
In this article, we’ll showcase how ten cities around the world are using technology to optimize and promote eco-friendly urban policies and practices.
Singapore
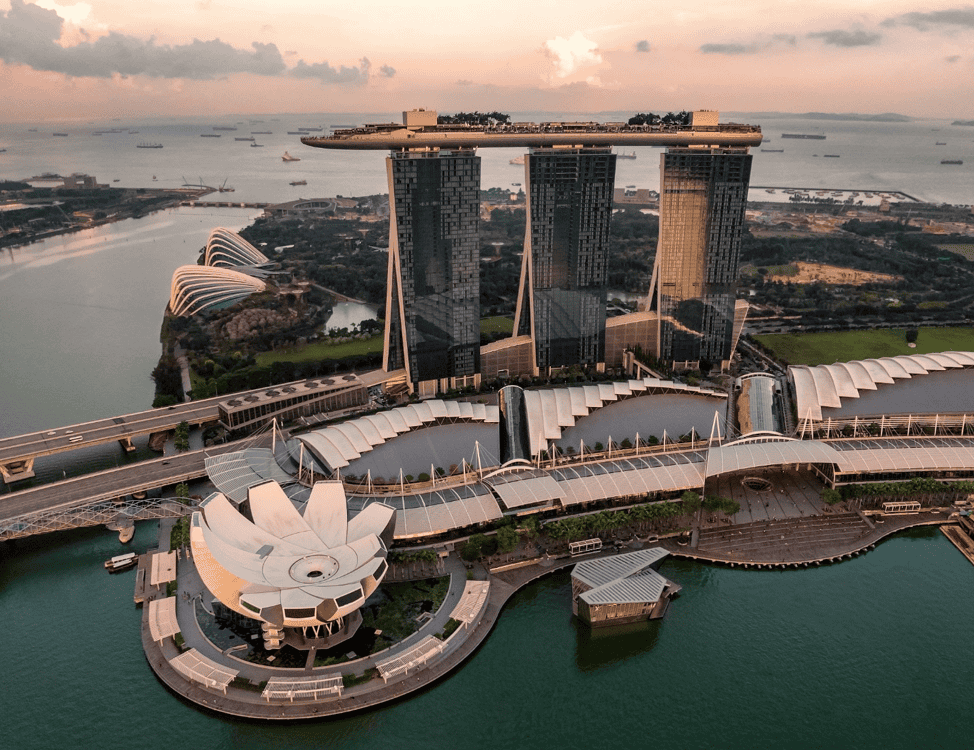
According to an estimate from the ‘Senseable City’ lab at MIT, Singapore’s transition to driverless, shared vehicles can enable the city to eliminate 80% of its 1.3 million parking spaces.
The city’s Green Plan 2030 aims to use the latest available technology to facilitate Singapore’s national agenda on sustainable development and goal towards net zero emissions.
Key targets include major investments in Green Finance, building up the financial sector’s resilience to environmental risks, as well as to develop eco-friendly finance solutions.
Oslo

The perks of owning an electric vehicle in Oslo include free parking, charging and transport on ferries, as well as no sales tax and more than 2000 charging stations around the city.
With buildings accounting for approximately 40% of energy consumption globally, Oslo is utilising a wide range of smart sensors to control and monitor lighting, heating and cooling.
The Oslo Airport City project, a technologically-driven community which will take 30 years to build, will be powered entirely by renewable energy and smart management systems.
New York

Urban gardening companies grow fresh produce in smart greenhouses by using technology to monitor watering, cooling, heating and plant nutrition, and ultimately using less resources.
Touchscreen kiosks scattered around the city have replaced public phone booths and provide phone charging stations and digital access to useful city information.
New York’s Department of Environmental Protection launched an Automated Meter Reading system installed in more than 800,000 properties, enabling residents to optimize water use.
Chicago

As sensors collect real-time data on Chicago’s climate, air quality, noise and congestion, urban planners and policy makers can make more accurate decisions that improve citizens’ lives.
Customized energy-use dashboards sold by Chicago-based Goby enable building owners and tenants to be more efficient with cooling, heating and powering buildings.
The Chicago Center for Green Technology is the first municipal building renovation awarded by the U.S. Green Building Council and the largest green design educational center in the Midwest.
Copenhagen
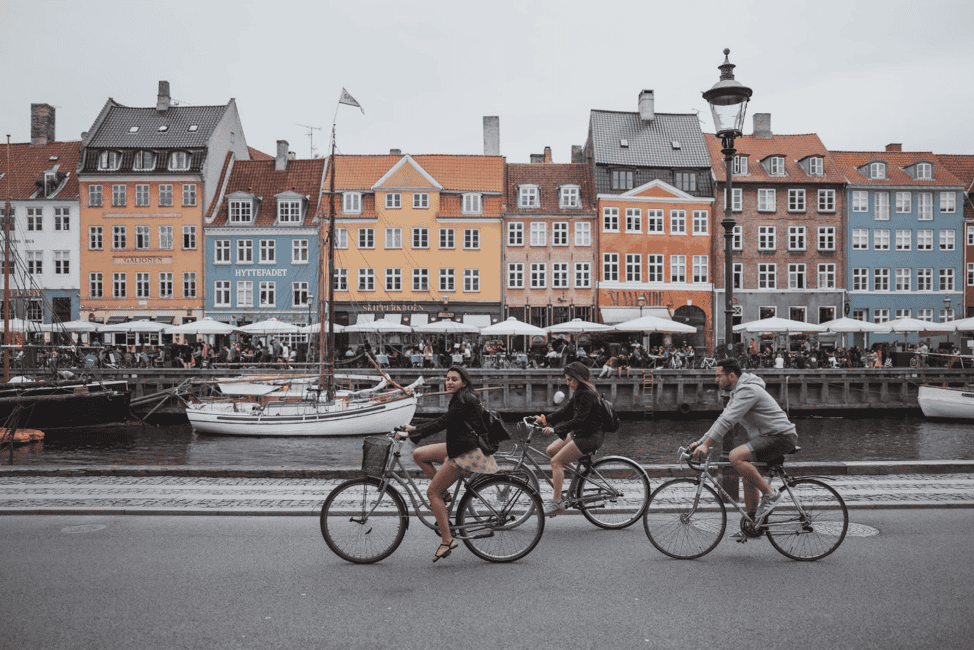
Connecting the city’s smart meters, parking spots, traffic lights and electric vehicle charging stations in real-time enabled more efficient services and reduced environmental impact.
Copenhagen is a great place for cyclists – half its residents bike to work – and the city partnered up with MIT’s Senseable City Lab to develop the Copenhagen Wheel Project.
The project aims to transform any ordinary bike into a feedback-providing device, collecting real-time data on pollution, traffic congestion and road conditions.
Barcelona

Smart street lights detect pedestrian activity and dim automatically when streets are empty, doubling up as wi-fi stations and providing free internet access throughout the city.
Internet of Things (IoT) technologies are used to monitor and control park irrigation and water levels in public fountains, achieving cost reductions and a 25% increase in water conservation.
Bins in this city are so smart they can detect hazardous material, suck up garbage in underground storage, reducing waste smells and noise pollution from collection vehicles.
Hong Kong
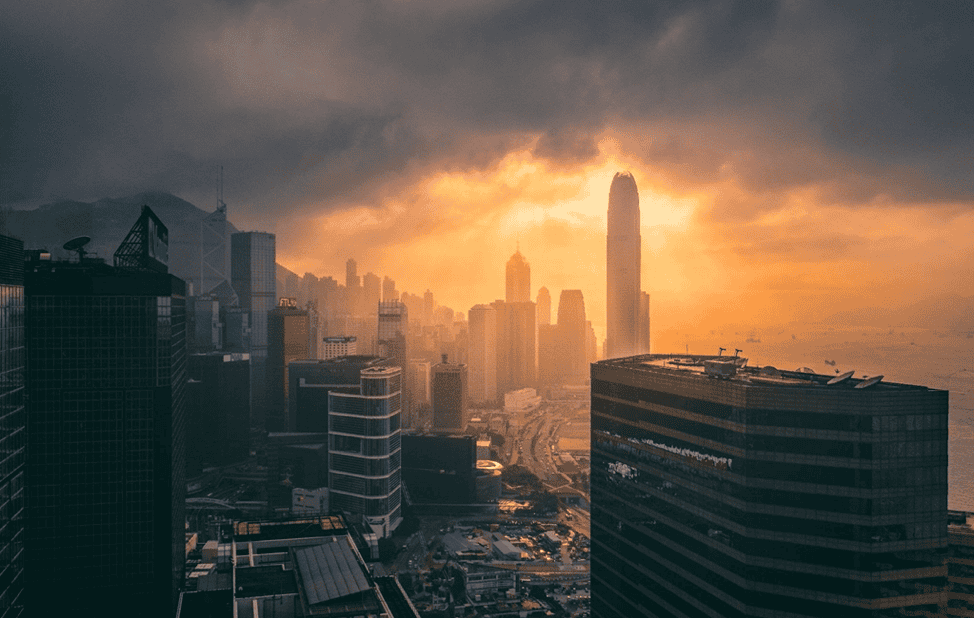

Residents can also benefit from the City Dashboard project, which is essentially a mobile-friendly interface providing real-time info on rainfall, traffic and parking availability.
Being one of the world’s most crowded places, Hong Kong’s leading building developers are looking to smart green technologies for construction projects of the future.
Incorporating new technologies for every step of the process – from design and architecture to engineering and sales – smart building development is cost-effective and eco-friendly.
Zurich
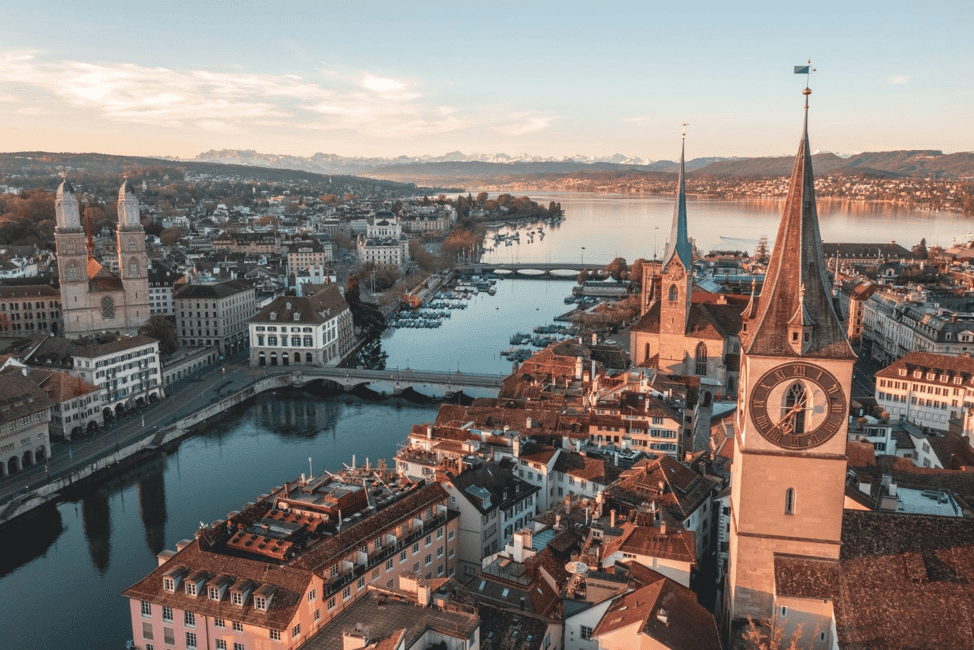

Through smart monitoring technologies, Zurich has achieved a significant reduction in CO2 emissions and has ensured that living spaces operate in harmony with the natural environment.
In 2016, Dutch engineering firm Arcadis placed Zurich at the top of a list of sustainable cities around the world due to its ambitious goal of using just 2000 watts per person by 2050.
The Green City project is Zurich’s first neighborhood to be constructed in compliance with the 2000 Watts Site certification criteria – and it is fully powered by renewable energy.
Amsterdam

There are few other places in the world embracing the smart city vision as seriously as Amsterdam, mainly because of the city’s Amsterdam Smart City initiative.
Founded in 2009, the collaborative effort between city authorities, universities, the private sector and residents has managed to use digital technology to optimize energy efficiency.
By digitizing and streamlining city services, the city has not only achieved faster and cheaper services for its residents, but also significantly reduced greenhouse emissions.
Digital nomads can easily work from outdoor public spaces as a result of the Zonspot project, which established solar-powered wi-fi hotspots throughout the city.
Berlin
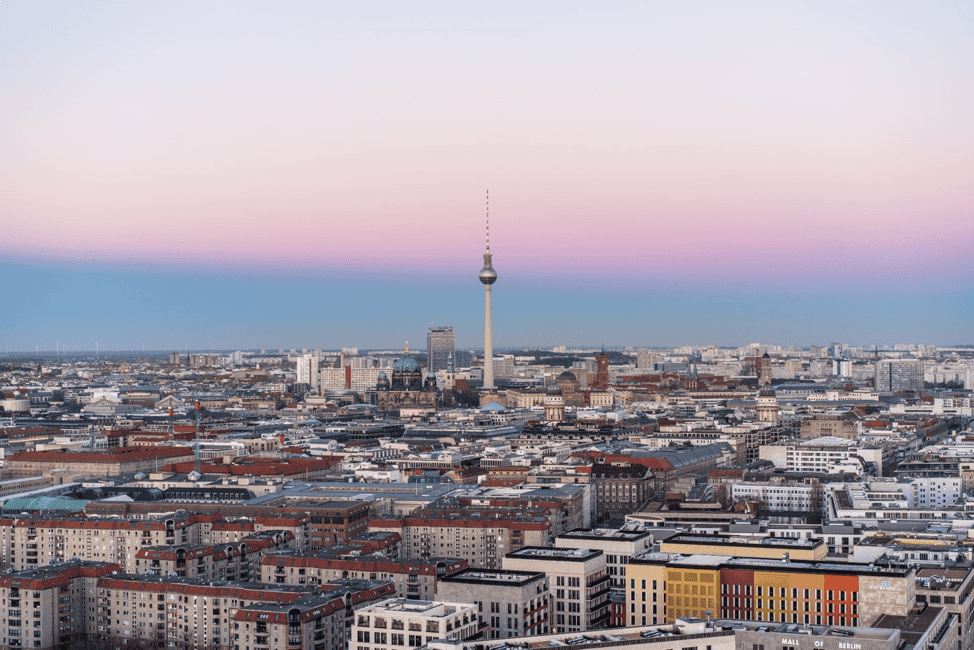

As of 2015, Berlin launched the Smart City Berlin Strategy, aiming to use advanced data-gathering solutions to increase resource efficiency and climate neutrality by 2050.
The city has prioritized ecological mobility by focusing on holistic transport concepts, transport sharing, electromobility, network integration and traffic control.
Berlin’s unique ecosystem of tech start-ups, incubators and venture capital availability make it an ideal city for developing the green tech solutions of a sustainable future.
At Bocasay, offshore outsourcing company, we develop smart IT solutions that empower businesses around the world. Have a tech project for the future we can help you with? Get in touch to find out how.